Kelvin Helmholtz instability
A non-hydrostatic configuration to demonstrate Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities.
A two-layer system with a large shear between the layers. The domain is two-dimensional, i.e. in the x-z plane, periodic in x and y, and there are no surface fluxes at the top or bottom, but a zone in the westernmost part of the domain, where temperature and velocity are relaxed towards the initial conditions. The initial conditions are two layers of equal thickness but different buoyancy moving to the east and relative to each other. At the layer interface a small disturbance is introduced such that in the simulation Kelvin-Helmholtz instability will show up.
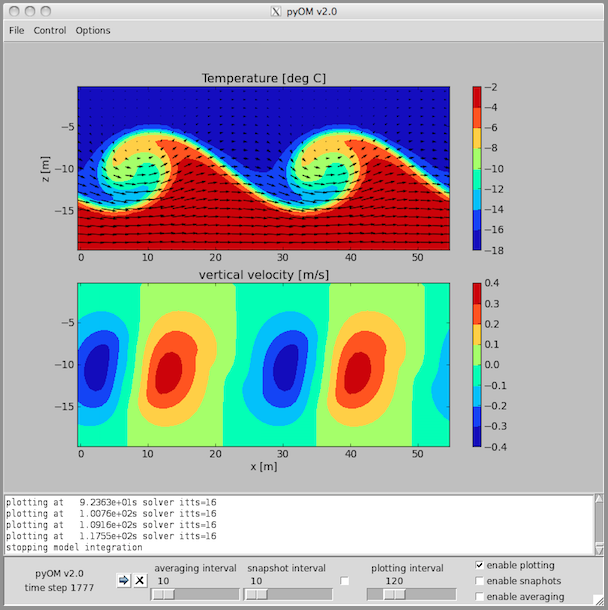
Configuration
Python front end kelv_helm1.py
Fortran front end kelv_helm1.f90
