|
Size: 4532
Comment:
|
Size: 4797
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| ## page was renamed from FEW3O/WWK ## page was renamed from WWK |
|
| Line 6: | Line 4: |
| = WWK-Wiki am IfM = At U Hamburg's wind-wave tank basic research is perfomed on air-sea interactions and their remote sensing. Fluxes of energy, momentum, gas and heat, along with the underlying small-scale processes, can be varied and studied. Frequent experimental campaigns are perfomed at the wind-wave tank, which aid in the development of new theories of air-sea interactions and of the remote sensing of the sea surface. |
|
| Line 9: | Line 5: |
| . {{attachment:UHH_WWK_Interior.jpg}} . ''The interior of U Hamburg' wind-wave tank, seen from its leeward end. Foto (c) M. Steinmetz 2002.'' |
= The Wind-Wave Tank of the University of Hamburg = At U Hamburg's wind-wave tank basic research is perfomed on air-sea interactions and their remote sensing. Fluxes of energy, momentum, gas and heat, along with the underlying small-scale processes, can be varied and studied. Frequent experimental campaigns are performed aid in the development of new theories on air-sea interactions and on the radar remote sensing of wind-roughended sea surfaces.<<BR>><<BR>> |
| Line 12: | Line 8: |
| The wind_wave tank was built in the early 1970s and is located in a hall at the Federal Institute of Waterways Engineering in Hamburg-Rissen. The water-filled part of the large facility is 24 m long and 1 m wide, and the air volume is 1 m high. The tank is filled with fresh water, a radial blower is used to generate wind speeds up to 25 m/s and a wave flap to generate long waves of frequencies between 0.7 Hz and 2.5 Hz.m/s erzeugt werden und mit einer Wellenklappe lange Wellen mit Frequenzen zwischen 0.7 Hz und 2.5 Hz. | |
| Line 14: | Line 9: |
| . {{attachment:UHH_WWK_Sketch.jpg}} . ''Schematic side view of the wind-wave tank; 1: diffusor; 2: beach; 3: radar antennas; 4: wave height and slope sensors; 5: rain generator; 6: laser optics; 7: microwave absorber; 8: propeller anemometer; 9: honeycomb; 10: wave flap; 11: radial blower.'' |
. {{attachment:WWK.jpg|UHH's wind-wave tank|width=60%}} . ~-''U Hamburg's wind-wave tank.''-~<<BR>><<BR>> |
| Line 17: | Line 12: |
| In the late 1990s, a rain generator was developed and installed to generate heavy rain of up to 300 mm/h on an area of 2.3 m². In the mid 2000s an air re-circulation was added and the tank was made air-tight, thereby allowing comprehensive gas exchange measurements. | The wind_wave tank was built in the early 1970s and is located in a hall at the Federal Institute of Waterways Engineering in Hamburg-Rissen. The water-filled part of the large facility is 24 m long and 1 m wide, and the air volume is 1 m high. The tank is filled with fresh water, a radial blower is used to generate wind speeds up to 25 m/s and a wave flap to generate long waves of frequencies between 0.7 Hz and 2.5 Hz.m/s erzeugt werden und mit einer Wellenklappe lange Wellen mit Frequenzen zwischen 0.7 Hz und 2.5 Hz.<<BR>><<BR>> |
| Line 19: | Line 14: |
| . {{attachment:UHH_WWK_windwaves.gif}} . ''Seitenansicht winderzeugter Wellen bei unterschiedlichen WIndgeschwindigkeiten.'' |
|
| Line 22: | Line 15: |
| The wind-wave tank is very well suited for experiments under controlled environmental conditions. E.g., in order to simulate biogenic films on the sea surface chemical model substances can be deployed, which form surface films of only one molecule thickness. The impact of those films on the small-scale wave and current field, and on the backscattered radar power, can be studied in great detail. Taking advantage of its flexible usage, the wind-wave tank can be well used to study a wealth of scientific aspects and to help in interpreting remotely sensed data. | . {{attachment:WWK_Regen2_Ziff.jpg|Sketch of the wwt|width=80%}} . ~-''Schematic side view of the wind-wave tank during campaigns with artificial rain; 1: wind tunnel; 2: beach; 3: radar antennas; 4: wave height and slope sensors; 5: laser optics; 6: rain generator; 7: honeycomb; 8: wave flap; 9: radial blower.''-~<<BR>><<BR>> In the late 1990s, a rain generator was developed and installed to generate heavy rain of up to 300 mm/h on an area of 2.3 m². In the mid 2000s, an air re-circulation was added for comprehensive gas exchange measurements.<<BR>><<BR>> . {{attachment:WWK-Rain.jpg|rain drops impinging on the water suface|width=60%}} . ~-''Photograph showing splash products caused by impinging rain drops.''-~<<BR>><<BR>> The wind-wave tank is very well suited for experiments under controlled environmental conditions. E.g., in order to simulate biogenic films on the sea surface chemical model substances can be deployed, which form surface films of only one molecule thickness. The impact of those films on the small-scale wave and current field, and on the backscattered radar power, can be studied in great detail. Taking advantage of its flexible usage, the wind-wave tank can be well used to study a wealth of scientific aspects and to help in interpreting remotely sensed data.<<BR>><<BR>> . {{attachment:WWK-Wind.jpg|windwaves|width=40%}} {{attachment:WWK-WindSlick.jpg|windwaves and slick|width=40%}} . ~-''Photographs showing the damping effect of a surfactant; left: wind-generated waves at 5m/s; right: same wind speed, but upper part covered by a surfactant.''-~<<BR>><<BR>> |
| Line 25: | Line 30: |
| . ''Synthetik-Apertur-Radar (SAR) Aufnahme des Südchinesischen Meers, die von Bord des Europäischen UMweltsatelliten ERS-1 aus am 14. Mai 1998 um 0252 UTC gemacht wurde ((c) ESA). DIe hellen Flecken im unteren linken Bereich werden durch Starkregen verursacht, die länglichen dunklen Bereiche im oberen Bereich durch marine Oberflächenfilme. Bildgröße 100 km x 105 km.'' | . ~-''Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Image of the South China Sea, acquired from the European ERS-1 satellite on 14 May 1998 at 02:52 UTC ((c) ESA). Bright patches in the lower left part were caused by heavy rain, the elongated dark patches in the upper left part by marine surface films. Image size 100 km x 105 km.''-~ |
| Line 50: | Line 55: |
| . {{attachment:Grünpfeil.jpg||height=30}} [[KFEW3O/WWK/WWKPraktikum|{{attachment:OzMess_b.jpg|KFEW3O/WWK/WWKPraktikum|height="30"}}]] . {{attachment:Grünpfeil.jpg||height=30}} [[KFEW3O/WWK/WWKPraktikum|Internal pages]] for participants. |
. {{attachment:KFEW3O/Grünpfeil.jpg||height=30}} [[ozmess|{{attachment:KFEW3O/OzMess_b.jpg|Ozeanische Messübungen|height="30"}}]] ...practicals ([[ozmess|for participants only]]) |
| Line 53: | Line 57: |
| ---- . {{attachment:Grünpfeil.jpg||height=30}} [[KFEW3O/WWK/WWKintern|{{attachment:intern_r.jpg|KFEW3O/WWK/WWKintern|height="30"}}]] ...to the internal pages [[KFEW3O/WWK/WWKintern|this way]]. |
----- . {{attachment:KFEW3O/Grünpfeil.jpg||height=30}} [[KFEW3O/WWK/WWKintern|{{attachment:KFEW3O/intern_l.jpg|WWKintern|height="30"}}]] ...internal WWK pages [[KFEW3O/WWK/WWKintern|this way]]. |
| Line 56: | Line 60: |
| . {{attachment:Grünpfeil.jpg||height=30}} ... back to the [[KFEW3O|main KFEW3O page]]... | . {{attachment:KFEW3O/Grünpfeil.jpg||height=30}} [[KFEW3O|{{attachment:KFEW3O/KFEW3O_l.jpg|KFEW3O|height="30"}}]]... back to the [[KFEW3O|main KFEW3O page]]... |
The Wind-Wave Tank of the University of Hamburg
At U Hamburg's wind-wave tank basic research is perfomed on air-sea interactions and their remote sensing. Fluxes of energy, momentum, gas and heat, along with the underlying small-scale processes, can be varied and studied. Frequent experimental campaigns are performed aid in the development of new theories on air-sea interactions and on the radar remote sensing of wind-roughended sea surfaces.
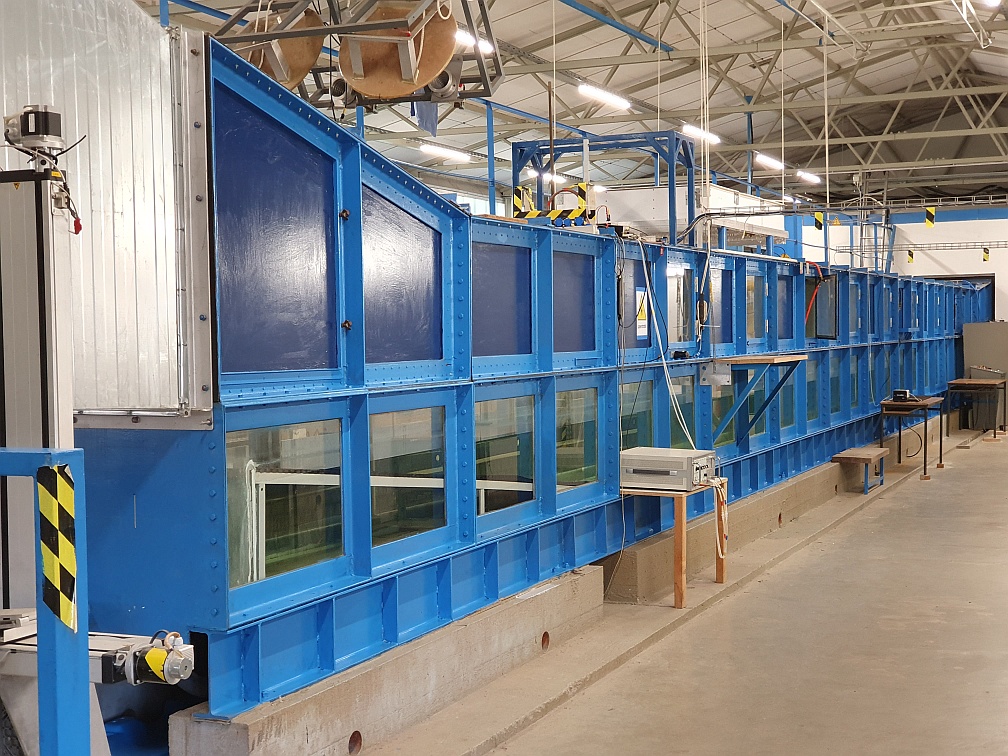

U Hamburg's wind-wave tank.
The wind_wave tank was built in the early 1970s and is located in a hall at the Federal Institute of Waterways Engineering in Hamburg-Rissen. The water-filled part of the large facility is 24 m long and 1 m wide, and the air volume is 1 m high. The tank is filled with fresh water, a radial blower is used to generate wind speeds up to 25 m/s and a wave flap to generate long waves of frequencies between 0.7 Hz and 2.5 Hz.m/s erzeugt werden und mit einer Wellenklappe lange Wellen mit Frequenzen zwischen 0.7 Hz und 2.5 Hz.
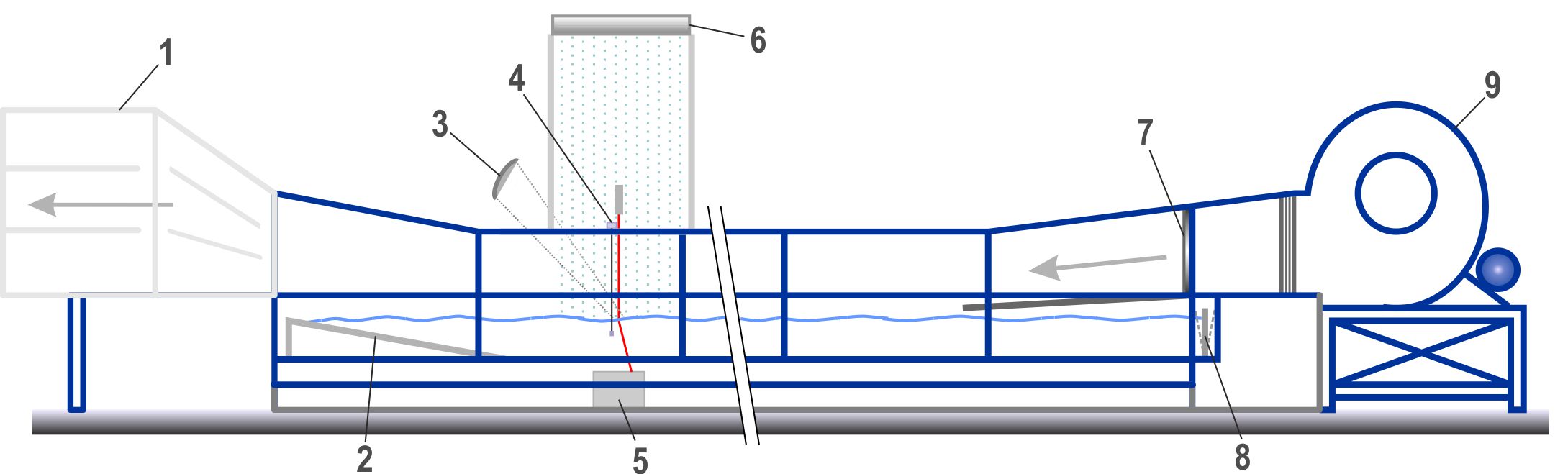
Schematic side view of the wind-wave tank during campaigns with artificial rain; 1: wind tunnel; 2: beach; 3: radar antennas; 4: wave height and slope sensors; 5: laser optics; 6: rain generator; 7: honeycomb; 8: wave flap; 9: radial blower.
In the late 1990s, a rain generator was developed and installed to generate heavy rain of up to 300 mm/h on an area of 2.3 m². In the mid 2000s, an air re-circulation was added for comprehensive gas exchange measurements.
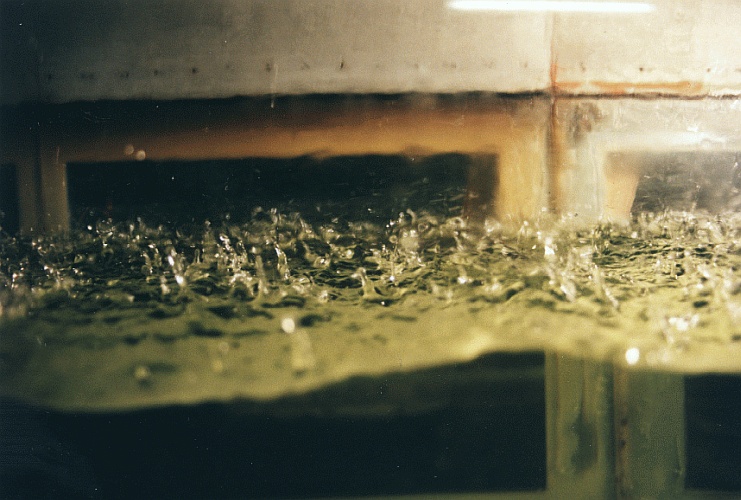

Photograph showing splash products caused by impinging rain drops.
The wind-wave tank is very well suited for experiments under controlled environmental conditions. E.g., in order to simulate biogenic films on the sea surface chemical model substances can be deployed, which form surface films of only one molecule thickness. The impact of those films on the small-scale wave and current field, and on the backscattered radar power, can be studied in great detail. Taking advantage of its flexible usage, the wind-wave tank can be well used to study a wealth of scientific aspects and to help in interpreting remotely sensed data.
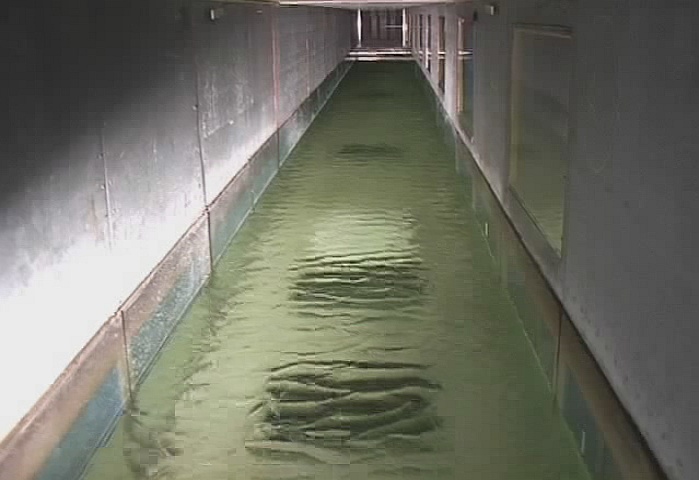
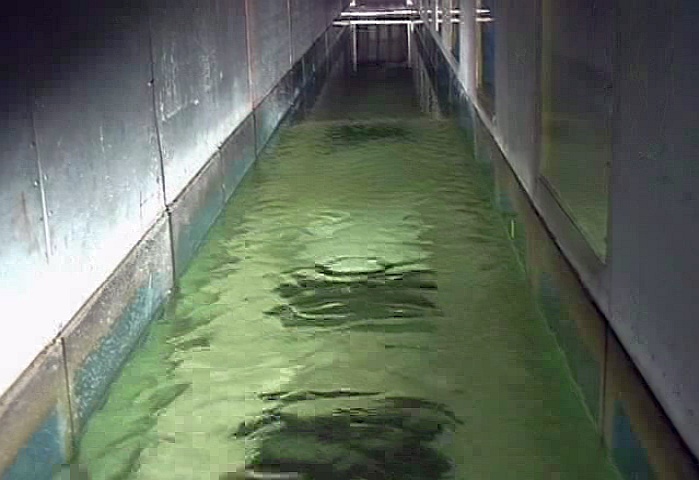


Photographs showing the damping effect of a surfactant; left: wind-generated waves at 5m/s; right: same wind speed, but upper part covered by a surfactant.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Image of the South China Sea, acquired from the European ERS-1 satellite on 14 May 1998 at 02:52 UTC ((c) ESA). Bright patches in the lower left part were caused by heavy rain, the elongated dark patches in the upper left part by marine surface films. Image size 100 km x 105 km.
Description
Description of UHH's wind-wave tank (M. Gade, 2003)
Previous Research
Practicals: ''Ozeanische Messübungen am WWK''
 ...practicals (for participants only)
...practicals (for participants only)

 ...internal WWK pages this way.
...internal WWK pages this way. 
 ... back to the main KFEW3O page...
... back to the main KFEW3O page...