|
Size: 718
Comment:
|
Size: 3644
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 11: | Line 11: |
| == 2 D Plots with Pylab == {{attachment:density.png}} {{{#!python from pylab import * # The seawater module is installed only for Python2.6.2: # module load Python/2.6.2 import seawater S=linspace(0,35) T=linspace(-2,35.0) rho=zeros((S.size,T.size)) for i,t in enumerate(T): rho[i,:]=seawater.dens(S,t) figure() CS = contour(S,T,rho,15,colors='k') clabel(CS, fontsize=8, inline=1) ylabel('Temperature [$^\circ$C]') xlabel('Salinity') title('Sea water density [kg/m$^3$]') show() savefig('density.png',dpi=75) }}} |
|
| Line 14: | Line 42: |
http://matplotlib.sourceforge.net/basemap/doc/html/ |
|
| Line 34: | Line 60: |
Don't forget to set the correct path for using Basemap on ZMAW systems {{{ module load python }}} == GMT == {{attachment:map.png}} [[http://gmt.soest.hawaii.edu/|GMT]] is an open source collection of ~60 tools for manipulating geographic and Cartesian data sets (including filtering, trend fitting, gridding, projecting, etc.) and producing publication quality scientific plots. In particular useful are the [[http://gmt.soest.hawaii.edu/gmt/examples/ex14/gmt_example_14.html|gridding routines]] which can be used for irregular sampled oceanographic as well as for satellite data. GMT can be easily applied together with Python using the [[http://docs.python.org/library/os.html|os module]]. {{{#!python import os os.system('pscoast -R4/12/52/57 -JM6i -P -B1g1 -Ggray -Df > map.ps') os.system('gv map.ps') }}} == Google Earth == {{attachment:600px-Google_earth_chlorophyll.png}} Documentation: http://code.google.com/apis/kml/documentation/ Chlorophyll data: http://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi/climatologies.pl Download png and make black transparent {{{ convert -transparent black A20020012007273.L3m_CU_CHLO_4.png A20020012007273.L3m_CU_CHLO_4_trans.png }}} Create ''.kml'' file {{{ <?xml version="1.0"?> <kml xmlns="http://earth.google.com/kml/2.1"><Document><name>Chlorophyll Climatology</name> <Folder> <Snippet maxLines="0"/> <name>MODIS</name> <ScreenOverlay> <name>UHH Logo</name> <color>ffffffff</color> <visibility>1</visibility> <Icon> <href>http://www.ifm.uni-hamburg.de/logo_uhh_neu.gif</href> </Icon> <overlayXY x="0" y="1" xunits="fraction" yunits="fraction"/> <screenXY x="5" y="5" xunits="pixels" yunits="insetPixels"/> <size x="90" y="90" xunits="pixel" yunits="pixel"/> </ScreenOverlay> <LookAt> <longitude>8</longitude> <latitude>53</latitude> <altitude>2000000</altitude> <heading>0</heading> </LookAt> <Folder> <Snippet maxLines="0"/> <name>Chlorophyll</name><GroundOverlay> <name>2002-2007</name> <visibility>1</visibility><color>ffffffff</color> <Icon><href>A20020012007273.L3m_CU_CHLO_4_trans.png</href></Icon> <LatLonBox><north>90</north><south>-90</south><east>180</east><west>-180</west></LatLonBox> </GroundOverlay></Folder></Folder></Document></kml> }}} == Grads == http://opengrads.org/wiki/index.php?title=PyGrADS_Interactive_Shell |
Visualisation
2 D Plots with Pylab
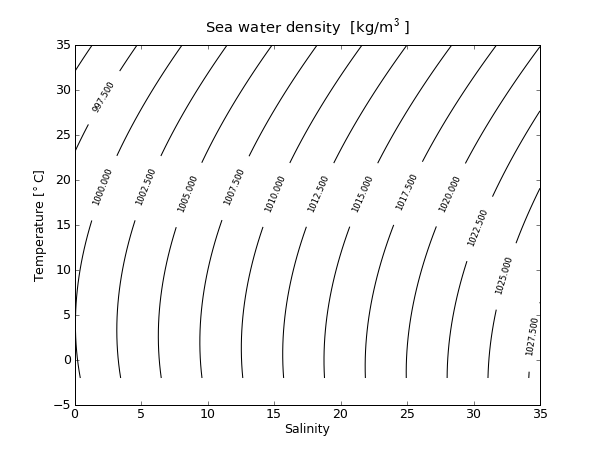
1 from pylab import *
2 # The seawater module is installed only for Python2.6.2:
3 # module load Python/2.6.2
4 import seawater
5
6 S=linspace(0,35)
7 T=linspace(-2,35.0)
8
9 rho=zeros((S.size,T.size))
10
11 for i,t in enumerate(T):
12 rho[i,:]=seawater.dens(S,t)
13
14 figure()
15 CS = contour(S,T,rho,15,colors='k')
16 clabel(CS, fontsize=8, inline=1)
17 ylabel('Temperature [$^\circ$C]')
18 xlabel('Salinity')
19 title('Sea water density [kg/m$^3$]')
20 show()
21 savefig('density.png',dpi=75)
Basemap
The matplotlib basemap toolkit is a library for plotting 2D data on maps in Python.
Don't forget to set the correct path for using Basemap on ZMAW systems
module load python
GMT
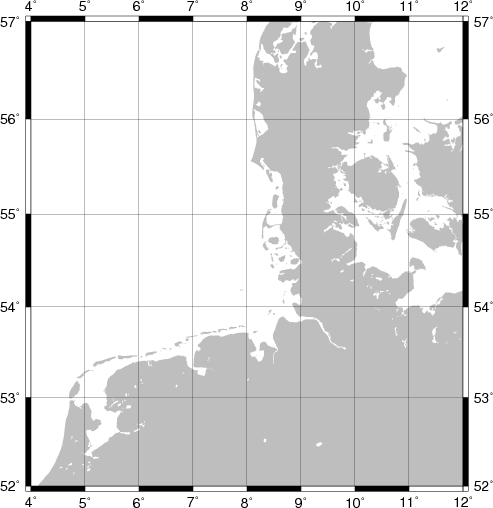
GMT is an open source collection of ~60 tools for manipulating geographic and Cartesian data sets (including filtering, trend fitting, gridding, projecting, etc.) and producing publication quality scientific plots.
In particular useful are the gridding routines which can be used for irregular sampled oceanographic as well as for satellite data.
GMT can be easily applied together with Python using the os module.
Google Earth
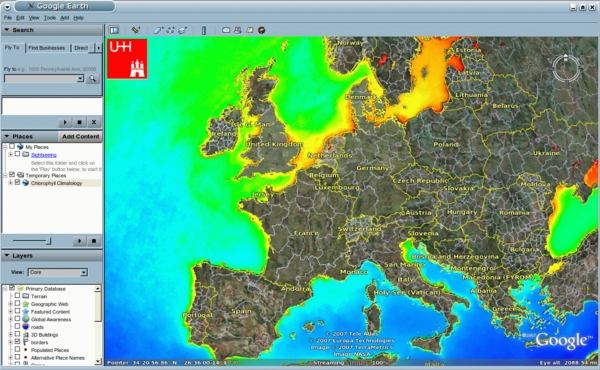
Documentation:
http://code.google.com/apis/kml/documentation/
Chlorophyll data:
http://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi/climatologies.pl
Download png and make black transparent
convert -transparent black A20020012007273.L3m_CU_CHLO_4.png A20020012007273.L3m_CU_CHLO_4_trans.png
Create .kml file
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<kml xmlns="http://earth.google.com/kml/2.1"><Document><name>Chlorophyll Climatology</name>
<Folder>
<Snippet maxLines="0"/>
<name>MODIS</name>
<ScreenOverlay>
<name>UHH Logo</name>
<color>ffffffff</color>
<visibility>1</visibility>
<Icon>
<href>http://www.ifm.uni-hamburg.de/logo_uhh_neu.gif</href>
</Icon>
<overlayXY x="0" y="1" xunits="fraction" yunits="fraction"/>
<screenXY x="5" y="5" xunits="pixels" yunits="insetPixels"/>
<size x="90" y="90" xunits="pixel" yunits="pixel"/>
</ScreenOverlay>
<LookAt>
<longitude>8</longitude>
<latitude>53</latitude>
<altitude>2000000</altitude>
<heading>0</heading>
</LookAt>
<Folder> <Snippet maxLines="0"/>
<name>Chlorophyll</name><GroundOverlay> <name>2002-2007</name>
<visibility>1</visibility><color>ffffffff</color>
<Icon><href>A20020012007273.L3m_CU_CHLO_4_trans.png</href></Icon>
<LatLonBox><north>90</north><south>-90</south><east>180</east><west>-180</west></LatLonBox>
</GroundOverlay></Folder></Folder></Document></kml>
Grads
http://opengrads.org/wiki/index.php?title=PyGrADS_Interactive_Shell
