|
Size: 3293
Comment:
|
Size: 6414
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 9: | Line 9: |
| = Input/Output = | = Input/output and data formats = |
| Line 11: | Line 11: |
| This lesson deals with the ways of reading and writing data | This lesson deals with the ways of reading and writing data in different formats |
| Line 78: | Line 78: |
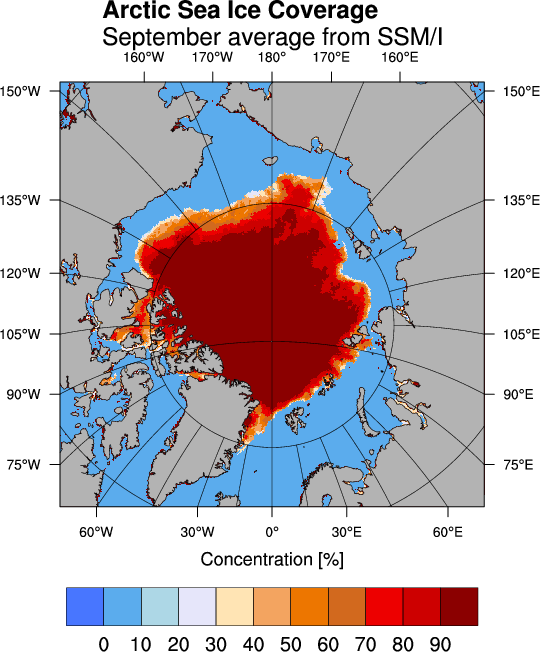
| [[http://www.pyngl.ucar.edu/|PyNIO]] is a Python package that allows read and/or write access to a variety of data formats using an interface modelled on [[http://www.unidata.ucar.edu/software/netcdf/|netCDF]]. The following example demonstrates how to use the [[http://www.pyngl.ucar.edu/|PyNGL]] module to read and display sea ice concentration data. {{{#!python import os from scipy import array,arange,nan from PyNGL import Ngl from PyNGL import Nio def Ngl_map(C,lat,lon,psfile): rlist = Ngl.Resources() rlist.wkColorMap = 'posneg_1' wks_type = "ps" wks = Ngl.open_wks(wks_type,psfile,rlist) resources = Ngl.Resources() resources.sfXArray = lon[:,:] resources.sfYArray = lat[:,:] resources.mpProjection = "Stereographic" resources.mpDataBaseVersion = "MediumRes" resources.mpLimitMode = "LatLon" resources.mpMinLonF = 0 resources.mpMaxLonF = 360 resources.mpMinLatF = 65 resources.mpMaxLatF = 90 resources.mpCenterLonF = 0. resources.mpFillOn = True igray = Ngl.new_color(wks,0.7,0.7,0.7) resources.mpFillColors = [0,-1,igray,-1] resources.cnLineDrawOrder = "Predraw" resources.cnFillOn = True resources.cnFillDrawOrder = "Predraw" resources.cnLineLabelsOn = False resources.nglSpreadColorStart = 8 resources.nglSpreadColorEnd = -2 resources.cnLevelSelectionMode = "ExplicitLevels" # Define own levels. resources.cnLevels = arange(0.,100,10) resources.lbTitleString = 'Concentration [%]' resources.lbOrientation = "Horizontal" resources.cnFillMode = "RasterFill" resources.cnLinesOn = False resources.tiMainString = "~F22~Arctic Sea Ice Coverage~C~~F21~September average from SSM/I" map = Ngl.contour_map(wks,C[:,:],resources) grid = Nio.open_file('grid_north_12km.nc') lat=array(grid.variables['latitude']) lon=array(grid.variables['longitude']) nc = Nio.open_file('climatology_09.nc') C=array(nc.variables['concentration'])[0,:,:].astype(float) Ngl_map(C,lat,lon,'map') os.system('gv map.ps &') }}} The data files can be downloaded from the [[ftp://ftp.ifremer.fr/ifremer/cersat/products/gridded/psi-concentration/data|ftp server]] of the [[http://cersat.ifremer.fr/|Center for Satellite Exploitation and Research (CERSAT)]] which is one of the major world data centers for oceanography. The September mean sea ice concentration values derived from the [[http://nsidc.org/data/docs/daac/ssmi_instrument.gd.html|Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I)]] are stored in the netCDF file [[ftp://ftp.ifremer.fr/ifremer/cersat/products/gridded/psi-concentration/data/arctic/climatology/netcdf/climatology_09.nc.Z|climatology_09.nc]] . Compressed data with the extension ({{{.Z .gz}}} can be uncompressed using {{{uncompress}}} or {{{gunzip}}}. {{attachment:september.png}} |
Contents
Input/output and data formats
This lesson deals with the ways of reading and writing data in different formats
Basic Python
The file object can be used for reading and writing plain text as well as unformatted binary data. The following code writes a message in the file with the name out.txt, reads and print the data
write() writes a string to the file
read() reads complete file
read(N) reads N bytes
readlines() reads the file with linebreaks
readline() reads only the next line
Pickle
The pickle module implements an algorithm for serializing and de-serializing a Python object structure. Pickling is the process whereby a Python object hierarchy is converted into a byte stream, and unpickling is the inverse operation, whereby a byte stream is converted back into an object hierarchy. The cPickle module is a much faster implementation and should be preferred.
Comma Separated Values
The so-called CSV (Comma Separated Values) format is the most common import and export format for spreadsheets (Excel) and databases. The csv module enables CSV file reading and writing
NumPy/SciPy
HDF
NASA's standard file format, the http://hdf.ncsa.uiuc.edu/index.html is a self-describing data format. HDF files can contain binary data and allow direct access to parts of the file without first parsing the entire contents.
The HDF versions 4 and 5 are not compatible.
Different modules are available for reading and writing HDF files
pyhdf
pyhdf is a python interface to the NCSA HDF4 library.
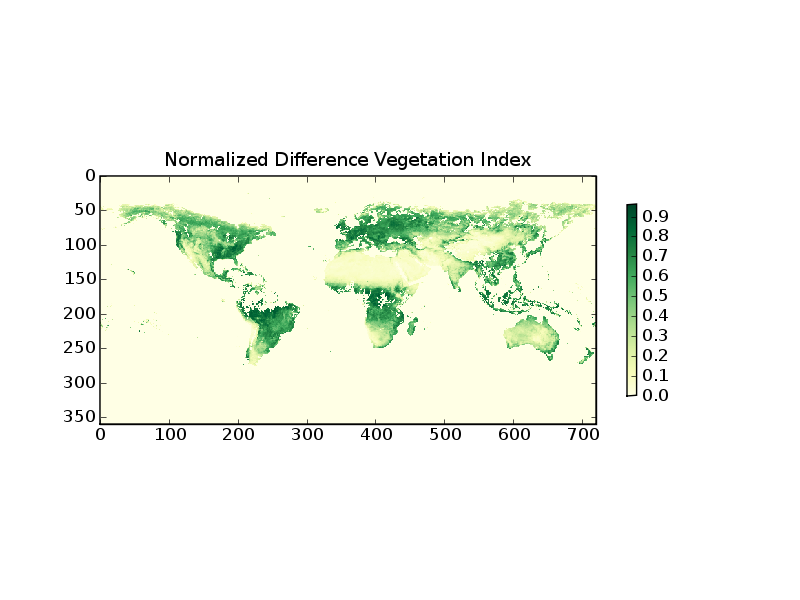
The following example demonstrates how to read level-3 data from the Multi-angle Imaging Spectral Radiometer (MISR) on the Terra Satellite
1 from scipy import array
2 from pylab import imshow,colorbar,title,savefig
3 from pyhdf.SD import SD
4
5 f=SD('MISR_AM1_CGLS_MAY_2007_F04_0025.hdf')
6 print f.datasets().keys()
7 data=array(f.select('NDVI average').get())
8 data[data<0]=0
9
10 imshow(data,interpolation='nearest',cmap=cm.YlGn)
11 colorbar(shrink=0.5)
12 title('Normalized Difference Vegetation Index')
Line 5 opens the HDF file object. line 6 prints the keywords of the included datasets. From this one can identify the keyword for the desired parameter. Line 7 reads the data in a SciPy array. Line 8 selects the negative (bad and missing) data and sets them to zero.
netCDF
PyNIO is a Python package that allows read and/or write access to a variety of data formats using an interface modelled on netCDF.
The following example demonstrates how to use the PyNGL module to read and display sea ice concentration data.
1 import os
2 from scipy import array,arange,nan
3 from PyNGL import Ngl
4 from PyNGL import Nio
5
6 def Ngl_map(C,lat,lon,psfile):
7 rlist = Ngl.Resources()
8 rlist.wkColorMap = 'posneg_1'
9 wks_type = "ps"
10 wks = Ngl.open_wks(wks_type,psfile,rlist)
11 resources = Ngl.Resources()
12 resources.sfXArray = lon[:,:]
13 resources.sfYArray = lat[:,:]
14 resources.mpProjection = "Stereographic"
15 resources.mpDataBaseVersion = "MediumRes"
16 resources.mpLimitMode = "LatLon"
17 resources.mpMinLonF = 0
18 resources.mpMaxLonF = 360
19 resources.mpMinLatF = 65
20 resources.mpMaxLatF = 90
21 resources.mpCenterLonF = 0.
22 resources.mpFillOn = True
23 igray = Ngl.new_color(wks,0.7,0.7,0.7)
24 resources.mpFillColors = [0,-1,igray,-1]
25 resources.cnLineDrawOrder = "Predraw"
26 resources.cnFillOn = True
27 resources.cnFillDrawOrder = "Predraw"
28 resources.cnLineLabelsOn = False
29 resources.nglSpreadColorStart = 8
30 resources.nglSpreadColorEnd = -2
31 resources.cnLevelSelectionMode = "ExplicitLevels" # Define own levels.
32 resources.cnLevels = arange(0.,100,10)
33 resources.lbTitleString = 'Concentration [%]'
34 resources.lbOrientation = "Horizontal"
35 resources.cnFillMode = "RasterFill"
36 resources.cnLinesOn = False
37 resources.tiMainString = "~F22~Arctic Sea Ice Coverage~C~~F21~September average from SSM/I"
38 map = Ngl.contour_map(wks,C[:,:],resources)
39
40 grid = Nio.open_file('grid_north_12km.nc')
41 lat=array(grid.variables['latitude'])
42 lon=array(grid.variables['longitude'])
43 nc = Nio.open_file('climatology_09.nc')
44 C=array(nc.variables['concentration'])[0,:,:].astype(float)
45 Ngl_map(C,lat,lon,'map')
46 os.system('gv map.ps &')
The data files can be downloaded from the ftp server of the Center for Satellite Exploitation and Research (CERSAT) which is one of the major world data centers for oceanography.
The September mean sea ice concentration values derived from the Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) are stored in the netCDF file climatology_09.nc . Compressed data with the extension (.Z .gz can be uncompressed using uncompress or gunzip.