|
Size: 2208
Comment:
|
Size: 4703
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 27: | Line 27: |
| == Scenario == | |
| Line 30: | Line 31: |
| * Atmospheric influence is ignored. * No exchange with deeper ocean layers and immediate mixing * Heat balance at the sea surface: Short wave incoming radiation + long wave outgoing radiation * Q_SW + Q_LW = Q_srf |
* No atmosphere * No exchange with deeper ocean layers, immediate mixing * Heat balance at the sea surface: Short wave incoming radiation + long wave outgoing radiation {{{#!latex $ Q_{SW}^{\downarrow} + Q_{LW}^{\uparrow} = Q_{srf} $ }}} * Numerics: forward-in-time integration, finite differences * {{{#!latex $\frac{\partial T_{ml}}{\partial t}\rho_w c_w h_{ml}=Q_{srf}$ }}} == Research questions == Compute the time evolution of the ocean mixed layer temperature ''T_ml(t)'' for different ''h_ml'', initial temperatures ''T_ml(t=0)'', and short wave insolation ''Q_SW''. Estimate the typical time scale for stationarity and select appropriate time step ''delta_t'' for model integration. Change insolation after the model has reached stationarity. == Source code == [[/Gruppe1]] Execute with '''ipython -pylab''' and '''run model1.py''': {{{#!python from pylab import * #model1.py #LK 2010 # model setup time iter=1000 # number of iterations dt=60*60*24.0 # time step one day [s] #model setup space h_ml=10. # oceanic mixed layer depth [m] # physical constants T0=273.13 # zero degrees in [K] sig=5.67e-8 # Stefan-Boltzmann constant [W/m^2/K^4] # sea water albedo_sw=0.06 # short wave oceanic albedo eps_sw=0.97 # long wave oceanic emissivity sig=5.67e-8 # Stefan-Boltzmann constant [W/m^2/K^4] rho_sw=1024.0 # sea water density Cp_sw=4000. # Oceanic heat capacity [J/Kg/K] #Forcing data I=400.0 # short wave insolation [W/m^2] #Prognostic variables T_ml=zeros(iter) # oceanic mixed layer temperature [K] T_ml[0]=12.0 # initial temperature #Model integration for i in range(iter-1): Q1=(1-albedo_sw)*I # absorbed short wave radiation Q2=-eps_sw*sig*(T_ml[i]+T0)**4 # emitted long wave radiation T_ml[i+1]=T_ml[i]+(((Q1+Q2)*dt)/(h_ml*Cp_sw*rho_sw)) if i==500: # Change forcing data after 600 days I=380.0 # Display results figure(1) plot(T_ml) xlabel('Time [days]') ylabel(r'Temperature $T_{ml}$ [$^\circ$ C]') text(50,12.5,r'Initial temperature $T_{ml}=12^\circ$C') text(50,12.7,r'Short wave insolation $I=400$ W/m$^2$') text(500,14.0,r'Short wave insolation $I=380$ W/m$^2$') savefig('lesson1_results1.png',dpi=75) # Display 1/e time T_ml_scaled=(T_ml[501:999]-T_ml[999])/(T_ml[501]-T_ml[999]) # Normalize to 0-1 figure(2) plot(T_ml_scaled) grid() axis('tight') yticks((1,1/e),('1','1/e')) xlabel('Time after day 500 [days]') ylabel(r'Normalized temperature $T_{ml}^*$') savefig('lesson1_results2.png',dpi=75) show() }}} == Simulation results == |
Sea ice 2
Lecture, exercises and practical by Jun.-Prof. Dr. Lars Kaleschke
- Monday 13:30-15:00
- Room ZMAW 022
Description of the course
The lecture will cover the thermodynamic coupling between the sea ice, the ocean, and the atmosphere. It is designed for master-level students with moderate knowledge in numerics, scientific programming, and sea ice physics. A conceptual model of the Arctic will be derived and simulation results will be analysed. For didactical reasons the model will be developed from scratch and kept as simple as possible, but complex enough to learn about the basic principles of the thermodynamic interaction between the ocean, the ice and the atmosphere for climatic, oceanographic and meteorological studies.
Acknowledgments
This lecture is based on content taken from a lecture Sea ice modeling by Aike Beckmann (Univ. Hamburg, Summer 2009) and a short course on Ice-Ocean Modeling and Data Assimilation which was conducted by Frank Kauker and Michael Karcher (Univ. Bremen, 6-7 December 2006).
Lesson 1 - Ocean mixed layer and radiative forcing without sea ice and atmosphere
Introduction and references for download
Scenario
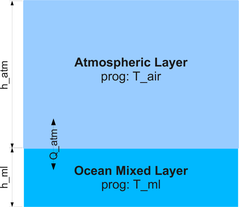
- Ocean mixed layer forced by shortwave radiation only
- No atmosphere
- No exchange with deeper ocean layers, immediate mixing
Heat balance at the sea surface: Short wave incoming radiation + long wave outgoing radiation
latex error! exitcode was 2 (signal 0), transscript follows:
- Numerics: forward-in-time integration, finite differences
latex error! exitcode was 2 (signal 0), transscript follows:
Research questions
Compute the time evolution of the ocean mixed layer temperature T_ml(t) for different h_ml, initial temperatures T_ml(t=0), and short wave insolation Q_SW.
Estimate the typical time scale for stationarity and select appropriate time step delta_t for model integration.
Change insolation after the model has reached stationarity.
Source code
Execute with ipython -pylab and run model1.py:
1 from pylab import *
2 #model1.py
3 #LK 2010
4
5 # model setup time
6 iter=1000 # number of iterations
7 dt=60*60*24.0 # time step one day [s]
8
9 #model setup space
10 h_ml=10. # oceanic mixed layer depth [m]
11
12 # physical constants
13 T0=273.13 # zero degrees in [K]
14 sig=5.67e-8 # Stefan-Boltzmann constant [W/m^2/K^4]
15 # sea water
16 albedo_sw=0.06 # short wave oceanic albedo
17 eps_sw=0.97 # long wave oceanic emissivity
18 sig=5.67e-8 # Stefan-Boltzmann constant [W/m^2/K^4]
19 rho_sw=1024.0 # sea water density
20 Cp_sw=4000. # Oceanic heat capacity [J/Kg/K]
21
22 #Forcing data
23 I=400.0 # short wave insolation [W/m^2]
24
25 #Prognostic variables
26 T_ml=zeros(iter) # oceanic mixed layer temperature [K]
27 T_ml[0]=12.0 # initial temperature
28
29
30 #Model integration
31 for i in range(iter-1):
32 Q1=(1-albedo_sw)*I # absorbed short wave radiation
33 Q2=-eps_sw*sig*(T_ml[i]+T0)**4 # emitted long wave radiation
34
35 T_ml[i+1]=T_ml[i]+(((Q1+Q2)*dt)/(h_ml*Cp_sw*rho_sw))
36
37 if i==500: # Change forcing data after 600 days
38 I=380.0
39
40 # Display results
41 figure(1)
42 plot(T_ml)
43 xlabel('Time [days]')
44 ylabel(r'Temperature $T_{ml}$ [$^\circ$ C]')
45 text(50,12.5,r'Initial temperature $T_{ml}=12^\circ$C')
46 text(50,12.7,r'Short wave insolation $I=400$ W/m$^2$')
47 text(500,14.0,r'Short wave insolation $I=380$ W/m$^2$')
48 savefig('lesson1_results1.png',dpi=75)
49
50 # Display 1/e time
51 T_ml_scaled=(T_ml[501:999]-T_ml[999])/(T_ml[501]-T_ml[999]) # Normalize to 0-1
52 figure(2)
53 plot(T_ml_scaled)
54 grid()
55 axis('tight')
56 yticks((1,1/e),('1','1/e'))
57 xlabel('Time after day 500 [days]')
58 ylabel(r'Normalized temperature $T_{ml}^*$')
59 savefig('lesson1_results2.png',dpi=75)
60 show()
Simulation results
Literature
Maykut, G.A. & N. Untersteiner, 1971: Some results from a time-dependent thermodynamic model of sea ice. J. Geophys. Res.,76, 1550-1575.
Semtner, A., 1976: A model for the thermodynamic growth of sea ice in numerical investigations of climate, J. Phys. Oceanogr, 6, 379-389.
Hibler III, W.D., 1979: A dynamic-thermodynamic sea ice model. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 9, 815-846.
Parkinson, C.L. & W.M. Washington, 1979: A large-scale numerical model of sea ice., J. Geophys. Res., 84, 311-337.
