Image statistics
The image is characterised by a probability density function (PDF). The PDF describes the probability of the occurrence of the discrete grey levels.
Example
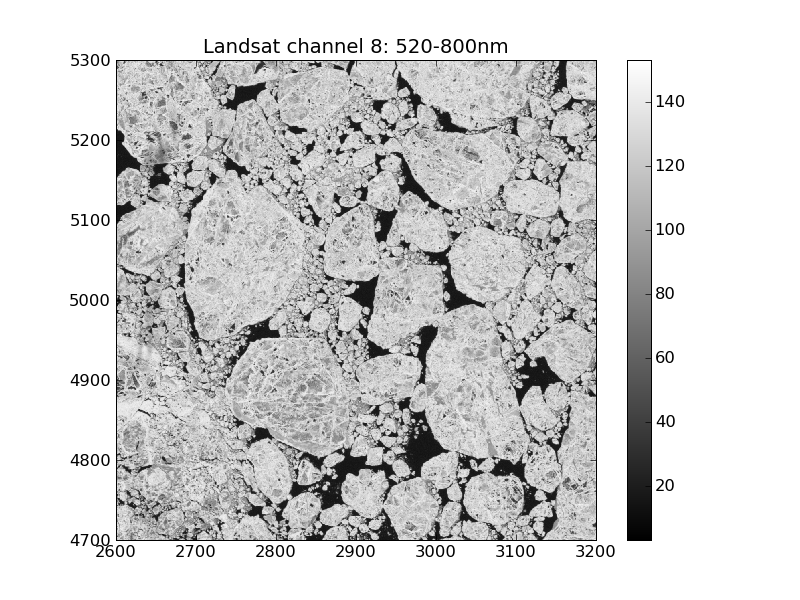

The following code calculates the PDF pdf(q) for a byte image img in the intervall [0,255]
The expression normed=True is used for the normalization of the PDF.
latex error! exitcode was 2 (signal 0), transscript follows:
The anti-derivative of the PDF is the cumulative density function (CDF).
latex error! exitcode was 2 (signal 0), transscript follows:
The cumulative sum can be calculated using
1 cdf=pdf.cumsum()
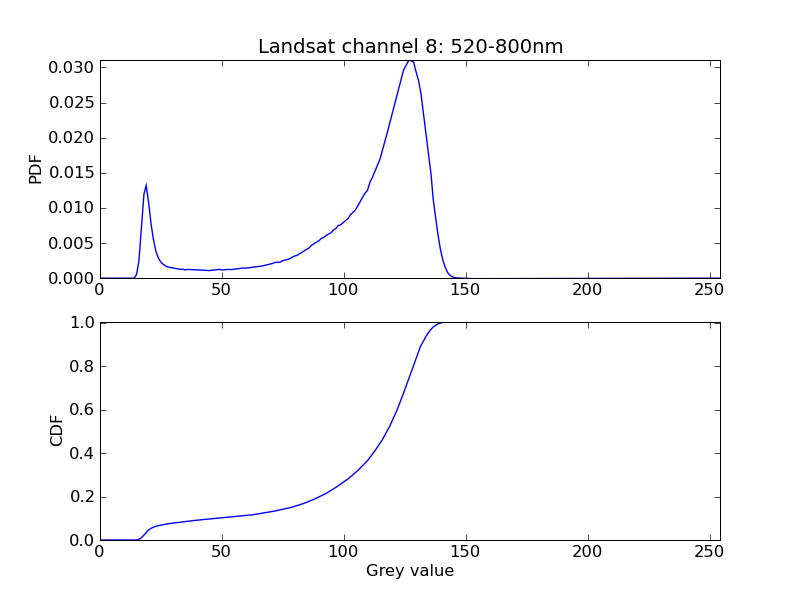
The probability of the occurence of grey levels in the interval [a,b] can be calculated from the CDF. In the example shown, the probability of grey levels to occur in the interval [12,25] according to the first peak is 0.068. So roughly 7% of the image pixels are in this grey level interval.