|
Size: 1384
Comment:
|
Size: 1972
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| = Aqua - Project Science= Aqua, Latin for water, is a NASA Earth Science satellite mission named for the large amount of information that the mission will be collecting about the Earth's water cycle, including evaporation from the oceans, water vapor in the atmosphere, clouds, precipitation, soil moisture, sea ice, land ice, and snow cover on the land and ice. Additional variables also being measured by Aqua include radiative energy fluxes, aerosols, vegetation cover on the land, phytoplankton and dissolved organic matter in the oceans, and air, land, and water temperatures. |
= Aqua - Project Science=
Aqua, Latin for water, is a NASA Earth Science satellite mission named for the large amount of information that the mission will be collecting about the Earth's water cycle, including evaporation from the oceans, water vapor in the atmosphere, clouds, precipitation, soil moisture, sea ice, land ice, and snow cover on the land and ice. Additional variables also being measured by Aqua include radiative energy fluxes, aerosols, vegetation cover on the land, phytoplankton and dissolved organic matter in the oceans, and air, land, and water temperatures.
AIRS: Atmospheric InfraRed Sounder
What is AIRS and what does the AIRS instrument suite measure?
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) is a facility instrument onboard the polar-orbiting Earth Observing System (EOS) Aqua satellite which was successfully launched on May 4, 2002. In combination with the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU-A) and the Humidity Sounder for Brazil (HSB), the AIRS instrument suite constitutes an innovative atmospheric sounding group of visible, infrared, and microwave sensors.
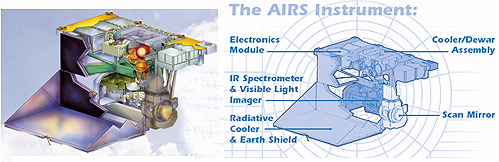
AIRS is a high spectral resolution spectrometer with 2378 bands in the thermal infrared (3.7 - 15.4 µm) and 4 bands in the visible (0.4 - 1.0 µm). These ranges have been specifically selected to allow determination of atmospheric temperature with an accuracy of 1°C in layers 1 km thick, and humidity with an accuracy of 20% in layers 2 km thick in the troposphere.
AIRS will make measurements of the Earth's atmosphere and surface that will allow scientists to improve weather prediction and to observe changes in Earth's climate.
For more information see the AIRS instrument guide: http://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/AIRS/additional/documentation/airs_instrument_guide.shtml
Quelle: http://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/AIRS/additional/instruments.shtml#1.
