|
Size: 1920
Comment:
|
Size: 1921
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 41: | Line 41: |
| Nearest neighbor gridding with 5 degree grid cell size, output is written to file {{grid.nc}} (GMT-netcdf): | Nearest neighbor gridding with 5 degree grid cell size |
| Line 49: | Line 50: |
| Line 51: | Line 51: |
| grdimage grid.nc -Rg -JG0/0/4i -Cg.cpt -K > out.ps | grdimage grid.nc -Rg -JG-45/0/4i -Cg.cpt -K > out.ps |
| Line 55: | Line 55: |
| pscoast -Rd -JG0/0/4i -B15g15 -Dc -Ggrey -P -O >> out.ps | pscoast -Rd -JG-45/0/4i -B15g15 -Dc -Gblack -P -O >> out.ps |
| Line 57: | Line 57: |
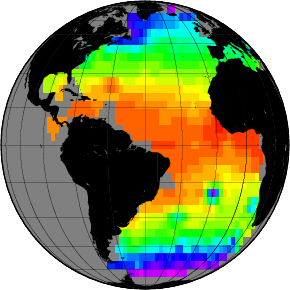
{{{ gv out.ps }}} {{attachment:out.png}} |
Contents
2-dimensional interpolation and gridding
2-dimensional interpolation and gridding is a common problem for the representation of measurements on a map. Usually measurements are taken at irregular sample points and not in a regular grid. There are various approaches for the problem and the best solution depends on the data.
In the following we will look at oceanographic parameters that have been measured with the Argo system.
Example data from Argo system
Data are provided at, i.e. ftp://ftp.ifremer.fr//ifremer/argo/
First we have to download the data. Here is a /download script that can be used to retrieve one month of Argo data.
We extract only the surface temperature to reduce the large amount of data. This /extract script generates an overview of the data and writes the surface temperature in a file lat_lon_T.tab which contains latitude, longitude and surface temperature. We can use this file in the following.
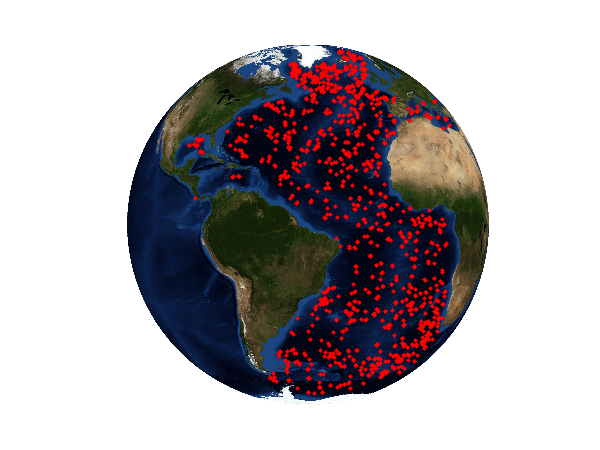
Argo positions of measurements
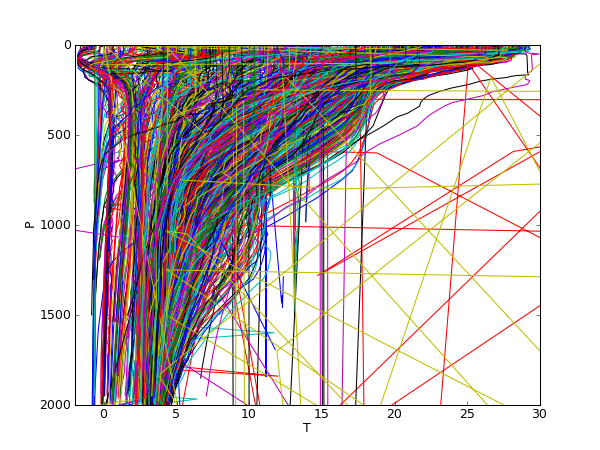
Measured temperature profiles (unfiltered data).
Tools for 2-dimensional interpolation and gridding
Python
GMT
Nearest neighbor gridding with 5 degree grid cell size
nearneighbor lat_lon_T.tab -Rd -I300m -S300m -N1 -Ggrid.nc
Generate color table:
makecpt -Crainbow -T-2/30/1 > g.cpt
grdimage grid.nc -Rg -JG-45/0/4i -Cg.cpt -K > out.ps
pscoast -Rd -JG-45/0/4i -B15g15 -Dc -Gblack -P -O >> out.ps
gv out.ps