|
Size: 3379
Comment:
|
Size: 3394
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 19: | Line 19: |
| First we have to download the data. Here is a script that can be used to download one month of data in a temporary directory called {{{tmp_dir}}}: | First we have to download the data. Here is a [[/download script]] that can be used to retrieve one month of data in a temporary directory called {{{tmp_dir}}}: |
| Line 51: | Line 51: |
| The next script generates an overview of the data and writes the surface temperature in a file called {{{lat_lon_T.tab}} which contains latitude, longitude and surface temperature. [[attachment:lat_lon_T.tab]] | The next script generates an overview of the data and writes the surface temperature in a file called {{{lat_lon_T.tab}}} which contains latitude, longitude and surface temperature. [[attachment:lat_lon_T.tab]] |
2-dimensional interpolation and gridding
2-dimensional interpolation and gridding is a common problem for the representation of measurements on a map. Usually measurements are taken at irregular sample points and not in a regular grid. There are various approaches for the problem and the best solution depends on the data.
In the following we will look at oceanographic parameters that have been measured with the Argo system.
Example: ARGO floats
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Argo_%28oceanography%29
Data are provided at, i.e. ftp://ftp.ifremer.fr//ifremer/argo/
First we have to download the data. Here is a /download script that can be used to retrieve one month of data in a temporary directory called tmp_dir:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2 import os,os.path
3 from ftplib import FTP
4
5 tmp_dir='/scratch/clisap/seaice/TMP/u242023/ARGO/'
6
7 ftp_adr='ftp.ifremer.fr'
8 ftp_dir='/ifremer/argo/geo/atlantic_ocean/2011/01/'
9
10 ftp = FTP(ftp_adr) # connect to host, default port
11 ftp.login() # user anonymous, passwd anonymous@
12 ftp.cwd(ftp_dir)
13
14 file_list=ftp.nlst()
15
16 for f in file_list:
17 urlfile='ftp://'+ftp_adr+ftp_dir+f
18 localfile=tmp_dir+f
19
20 if not(os.path.exists(localfile)):
21 print 'Getting file '+f
22 #We use curl instead of ftp.retrbinary for download
23 os.system("curl -s -k -o "+localfile+" "+urlfile)
24 else:
25 print 'file '+f+' exists'
26
27 ftp.close()
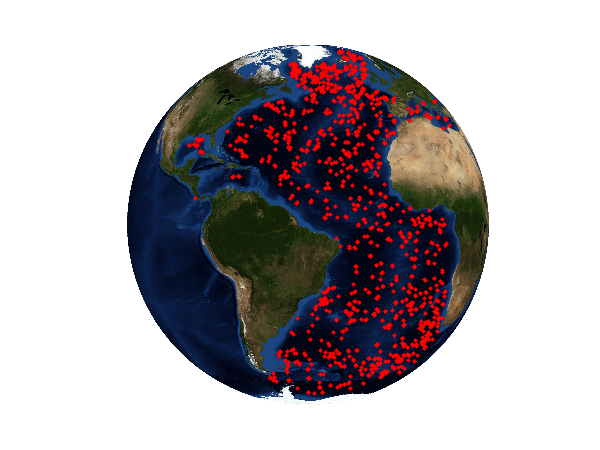
The next script generates an overview of the data and writes the surface temperature in a file called lat_lon_T.tab which contains latitude, longitude and surface temperature. lat_lon_T.tab
1 import scipy.io as io
2 import glob
3 from pylab import *
4 from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
5
6 tmp_dir='/scratch/clisap/seaice/TMP/u242023/ARGO/'
7
8
9 file_liste=glob.glob(tmp_dir+'*.nc')
10 D={}# Empty dictionary to store selected profiles
11 for f in file_liste:# Loop over all data
12
13
14 # Open netcdf data file
15 fid=io.netcdf_file(f,'r')
16
17 # Read content into variables
18 lat=fid.variables['LATITUDE'][:].copy()
19 lon=fid.variables['LONGITUDE'][:].copy()
20 T=fid.variables['TEMP'][:].copy()
21 P=fid.variables['PRES'][:].copy()
22
23 T[T>=99999]=nan # Set 99999.0 to "Not a Number"
24 P[P>=99999]=nan
25
26 (nr_profs,Z)=T.shape # Get dimension
27
28 for i in range(nr_profs):
29 D[(lon[i],lat[i])]=(T[i,:],P[i,:])
30
31 # Close data file
32 fid.close()
33
34 fid=open('lat_lon_T.tab','w')
35 for k in D.keys():# write position (lat,lon), surface temperature to file
36 fid.write(str(k[0])+'\t'+str(k[1])+'\t'+str(D[k][0][0])+'\n')
37 fid.close()
38 stop
39
40
41 # Draw map of positions
42 m = Basemap(projection='ortho',lon_0=-45,lat_0=0,resolution='l')
43 m.bluemarble()
44 for lon,lat in D.keys():
45 x,y=m(lon,lat) # Coordinate transfer
46 m.plot(x,y,'r.')
47
48 savefig('argo_position.png',dpi=150)
49
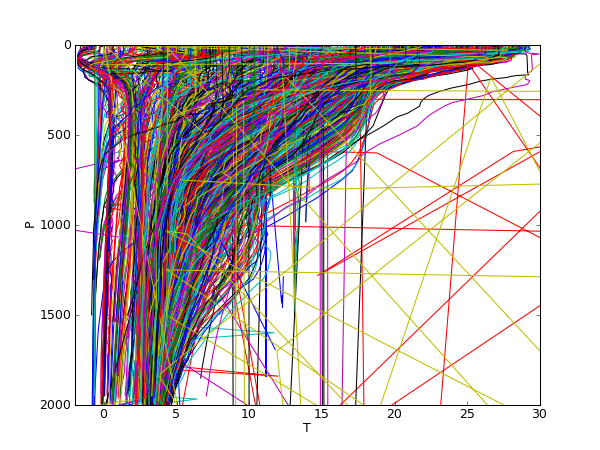
50 # Plot profiles
51 figure()
52 for k in D.keys():
53 # print k
54 plot(D[k][0][:],D[k][1][:])
55 axis([-2,30,2000,0])
56 xlabel('T')
57 ylabel('P')
58 show()
59 savefig('Argo_plot.png',dpi=75)
