|
Size: 3722
Comment:
|
Size: 4215
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 67: | Line 67: |
| Kevin Cowtan and Robert Way fill the gaps of the HadCRUT temperature data set by using satellite data. Compare their new reconstruction of surface temperature data to 1) independent in-situ observations and 2) reanalysis data | Kevin Cowtan and Robert Way fill the gaps of the HadCRUT temperature data set by using satellite data. Compare their new reconstruction of surface temperature data to independent in-situ observations and reanalysis data. |
| Line 69: | Line 69: |
| Their methods and data are freely available: | Cowtand and Way (2013) methods and data are freely available: |
| Line 74: | Line 74: |
| International Arctic Buoy Programme (IABP) data | Surface temperatures are available from the International Arctic Buoy Programme (IABP) website: |
| Line 78: | Line 78: |
| == Arctic sea ice thickness seasonal cycle == Ice mass balance buoys can measure the ice thickness. Calculate an average seasonal cycle and sea ice thickness trends! * http://imb.crrel.usace.army.mil/ * http://earthpy.org/near_realtime_data_from_arctic_ice_mass_balance_buoys.html |
=== Cowtan and Way (CW2013) reconstruction === |
| Line 88: | Line 82: |
| == == | * Review methods of Cowtan and Way (2013) * Write code to read and plot the data * Calculate trends and variabilites === Variations in Surface Air Temperature Observations in the Arctic === |
| Line 92: | Line 90: |
| == == | * Review methods of Rigor et al. (2000) * Write code to read and plot the gridded buoy data * Calculate trends and variabilites Reference: * [[http://iabp.apl.washington.edu/AirT/RigorEtal-SAT.pdf|Rigor, I., R. Colony, and S. Martin, 2000, Variations in Surface Air Temperature Observations in the Arctic, 1979 - 1997, J. Climate, Vol. 13, no 5, 896-914.]] === Data intercomparison === (advanced programming skills needed) * Write code to interpolate the different datasets in a common grid * Compare CW2013, buoy and reanalysis data (variability and trends) |
| Line 95: | Line 105: |
== Soil moisture == * Sampling bias [[/ProjectD]] |
|
| Line 100: | Line 117: |
| * prepare [[ftp://ftp.ifremer.fr/ifremer/cersat/products/gridded/psi-concentration/data/|sea ice data]] (Lars) :-) (CMIP5 data available) * prepare CMIP5 data (Alex) :-) |
* CW2013 :-) |
| Line 104: | Line 120: |
| * Stations :-) | * Bouy data :-) |
63-953 Climate and Satellite Data Analysis
MS Integrated Climate System Sciences
Date: 3.2.2014-7.2.2014
Place: Geom 1536c
Course objectives
The participants will learn to practically work with climate model, reanalysis, in-situ station and satellite data. Organized as a group project, the participants will further learn the principles of project management and shared software development.
Schedule
Monday
General Introduction
Stochastic analysis of time series.ipynb Monte carlo.ipynb GISSTEMP netcdf.ipynb datetimeobjects.ipynb Station data seasonal cycle.ipynb
Group work: develop a project plan and write a short technical proposal for your project.
Final report due by 15. March 2014
Obtain data and do preliminary analysis (e.g. data coverage).
Tuesday
Morning: Group presentations of project plan and preliminary analysis. Afternoon: implementation and project work
Wednesday
Morning: Group presentations of methods and code implementations Afternoon: Project work
Thursday
Morning: Group presentations of preliminary results Afternoon: Project work
Friday
Morning: final presenation of results and discussion Afternoon: evaluation and preparation of final report
Topics for group work
Coverage bias in the HadCRUT4 temperature series and its impact on recent temperature trends
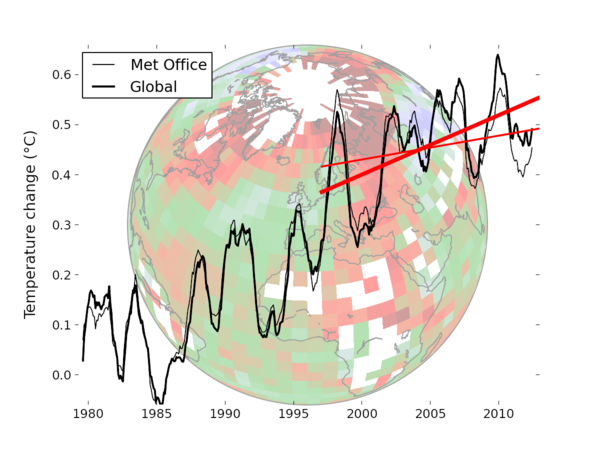
Kevin Cowtan and Robert Way fill the gaps of the HadCRUT temperature data set by using satellite data. Compare their new reconstruction of surface temperature data to independent in-situ observations and reanalysis data.
Cowtand and Way (2013) methods and data are freely available:
Surface temperatures are available from the International Arctic Buoy Programme (IABP) website:
Cowtan and Way (CW2013) reconstruction
- Review methods of Cowtan and Way (2013)
- Write code to read and plot the data
- Calculate trends and variabilites
Variations in Surface Air Temperature Observations in the Arctic
- Review methods of Rigor et al. (2000)
- Write code to read and plot the gridded buoy data
- Calculate trends and variabilites
Reference:
Data intercomparison
(advanced programming skills needed)
- Write code to interpolate the different datasets in a common grid
- Compare CW2013, buoy and reanalysis data (variability and trends)
Soil moisture
- Sampling bias
TODOs
Data
CW2013

ERA-Interim

NCEP

Bouy data

Final report
Template structure:
- Abstract
- Introduction: state of the art (literature), statement of the problem
- Methods and data
- Results
- Discussion
- Conlcusion
References
- Python Scripting for Computational Science, Hans Petter Langtangen, Springer (available in the ZMAW library)
