|
Size: 292
Comment:
|
Size: 7545
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 3: | Line 3: |
| Trockenprogrammierung: insbesondere die Konsistenz von Bildkoordinaten von ASAR und Freibord-Footprint klären die Klasseneinteilungen von ASAR und Freibordhöhen vergleichen Frage "welche Statistik will man anwenden" beantworten |
. Trockenprogrammierung: insbesondere die Konsistenz von Bildkoordinaten von ASAR und Freibord-Footprint klären die Klasseneinteilungen von ASAR und Freibordhöhen vergleichen Frage "welche Statistik will man anwenden" beantworten __'''Dienstag'''__ ---------- . '''Am Dienstag / Mittwoch erzeugtes Programm, das mit dem Zufallsgenerator sowohl die ASAR als auch Freibord - Daten erzeugt:''' {{{ #!python #project_plot.py from pylab import * from scipy import * import time,calendar,os,pipes,struct,string import random import scipy.ndimage as ndi from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse nk=5 #number of classes ndim=[1000,1000] #dimension of ASAR image in pixels res=12.5 freeb_asar_pixels=int(60./res)# footprint of freeboard is 60m fx0,fy0,fx2,fy2=[0.2,1.,1.,0.1] fx0,fy0,fx2,fy2=fx0*ndim[0],fy0*ndim[0],fx2*ndim[0],fy2*ndim[0] # freeboard coordinates from input file dist=sqrt((fx2-fx0)**2+(fy2-fy0)**2)*res fdist=172 #distance of two freeboard footprints is 172m nf=int(dist/fdist) fz_h=zeros(nf) #fz_h is the freeboard heights # produce a random array of freeboard heights for i in range(nf): fz_h[i]=random.random()*70 # the x,y positions of the freeboard footprints if fx2==fx0: fx=zeros(nf)+fx0 fy=linspace(0,ndim[1],nf) else: teta=(fy2-fy0)/(fx2-fx0) fx=linspace(fx0,fx2,nf) fy=(fx-fx0)*teta+fy0 #produce a random matrix of ASAR image classes (in 3 classes) a=zeros((ndim[0],ndim[1])) for i in range(ndim[0]): for j in range(ndim[1]): a[i,j]=int(random.random()*(nk)+1) #tranform from float to int #A=ndimage.gaussian_filter(a,1)+0.5 #B=A.astype(int) B=a.astype(int) #select the class of footprints from ASAR Image fz=zeros(nf) for i in range(nf): fz[i]=B[int(fx[i]-1),int(fy[i]-1)] #calculation of mean and standard deviation of freeboard heights in each class mean=zeros(nk) std_kl=zeros(nk) for kl in range(1,6): s=(fz==kl) fh_kl=fz_h[s] mean[kl-1]=fh_kl.sum()/fh_kl.shape[0] std_kl[kl-1]=std(fh_kl) #plot mean and error bar kl=arange(nk)+1 bar(kl,mean,yerr=std_kl,ecolor='r',align='center') axis('tight') savefig('kl_mean_std', orientation='portrait', format='png') #calculate correlation coefficient #corr=xcorr(fz,fz_h,normed=True)[1][nf] figure() #plot ASAR image class together with freeboard heights x=arange(nf) bar(x,fz,width=0.3,align='center') ylim(0,10) ax=twinx() plot(x,fz_h,'r+-',ms=10,linewidth=1) ylim(0,70) savefig('asar_fb', orientation='portrait', format='png') #axis('tight') #plot ASAR image with freeboard flight figure() ct=zeros((nf,4)) for i in range(nf): ct[i]=cm.gist_rainbow(int(fz_h[i])) ax=axes() ells=[Ellipse(xy=[fx[i],fy[i]],width=freeb_asar_pixels,height=freeb_asar_pixels) for i in xrange(nf)] n=0 for e in ells: ax.add_artist(e) e.set_clip_box(ax.bbox) e.set_alpha(0.5) e.set_facecolor(ct[n]) n+=1 gray() imshow(B,origin='lower',interpolation=None) hold(True) #plot(fx,fy,'r+-',linewidth=2) xlim(400,600) ylim(500,700) #xlim(0,1000) #ylim(0,1000) colorbar() savefig('asar_fb_track', orientation='portrait', format='png') #figure() #imshow(a) show() }}} Figure 1 (class - mean, standard deviation) / '''VIRTUELLE DATEN''' : {{attachment:kl_mean_std.png}} Figure 2 (asar, freboard) / '''VIRTUELLE DATEN''' : {{attachment:asar_fb.png}} '''Ziele für Mittwoch: ''' * Vom gestern erzeugte Graphen verfeinen * Programm für ASAR-Rohdaten & Freiborddaten Vergleich '''__Mittwoch__ ''' ---------- . '''Am Mittwoch erzeugtes Programm, das ASAR-Rohdaten und Freiborddaten (Zufallsgenerator), Faltungmaske 5x5 Pixel wurde benutzt:''' {{{ #!python #ASAR_raw.py from pylab import * from scipy import * import time,calendar,os,pipes,struct,string import random import scipy.ndimage as ndi from read_asar import * filename='/pf/u/u242027/SAR_raw/ASA_IMP_1PNDPA20060617_043346_000000162048_00362_22460_2136.N1' I=read_asar_imp(filename) ndim=[1000,1000] #dimension of ASAR image in pixels fx0,fy0,fx2,fy2=[200.,1000.,1000.,100.] # freeboard coordinates from input file cellsize=12.5 #12.5m pixelsize dist=sqrt((fx2-fx0)**2+(fy2-fy0)**2)*cellsize fdist=172 #distance of two freeboard footprints is 172m nf=dist/fdist fz_h=zeros(nf) #fz_h is the freeboard heights # produce a random array of freeboard heights for i in range(nf): fz_h[i]=random.random()*70 # the x,y positions of the freeboard footprints if fx2==fx0: fx=zeros(nf)+fx0 fy=linspace(0,ndim[1],nf) else: teta=(fy2-fy0)/(fx2-fx0) fx=linspace(fx0,fx2,nf) fy=(fx-fx0)*teta+fy0 B=I[1000:2000,1000:2000] mask=array(([1,1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2,1],[1,2,3,2,1],[1,2,2,2,1],[1,1,1,1,1]))/35. C=ndimage.convolve(B,mask,mode='reflect') #select the intensity value of footprints from ASAR Image fz=zeros(nf) for i in range(nf): pos=[int(fx[i]-1),int(fy[i]-1)] fz[i]=B[pos[0],pos[1]] #calculate correlation coefficient corr=xcorr(fz,fz_h,normed=True)[1][nf] figure() #plot ASAR image intensity together with freeboard heights x=arange(int(nf)) plot(x,fz,'b+-') ax=twinx() plot(x,fz_h,'r+-') savefig('asar_fb_track_RAW', orientation='portrait', format='png') #plot ASAR image with freeboard flight #figure() #plot(fx,fy,'r+-',linewidth=2) #colorbar() #imshow(B,origin='lower',interpolation=None) #hold(True) show() }}} Figure 1 (raw asar image, freeboard) / '''REELLE ASAR DATEN + VIRTUELLER FREIBORDDATENSATZ''' :: {{attachment:asar_fb_track_RAW.png}} '''''' '''Ziele für Donnerstag:''' * Farbtabelle für Freibordhöhen einbauen * Programpaketen der anderen Gruppe übernehmen und ins Programm einbauen * Testen und erste Ergebnisse liefern * Bericht schreiben '''__Donnerstag__ ''' ---------- . '''Am Donnerstag erzeugte Farbtabelle im 'project_plot.py' Program für Freibordhöhen:''' Figure 3 (asar, freeboard track) / '''VIRTUELLE DATEN''' : {{attachment:asar_fb_track.png}} Berichtteil: # Motivation (Fragestellung) # Daten (ICESat, ENVISAT) * - Zusammenbau Gruppe Weil es am Beginn des Projektes noch keine Ergebnisse von den anderen Gruppen zur Verfügung gestanden sind, hat unsere Gruppe in den ersten Projekttagen mit den aus dem Zufallsgenerator erzeugten Daten gearbeitet. Mit dem Zufallsgenerator "random.random()" haben wir Freibordhöhen () und ASAR Bild (). heißt ... # Methodik (Arbeitsschritten, Theorie, Input/Output) * - Zusammenbau Gruppe # Ergebnisse (Output, Statistik) * - Zusammenbau Gruppe Erste Gruppe hat eine Funktion geliefert x Zweite Gruppe hat ein Program geliefert # Diskussion (Hypothese bestätigt, widerlegt?) __Motivation__ Das Ziel von unserem Projekt ist es die Freibordhöhen im Gebiet des Weddellmeeres (Antarktis) zu klassifizieren. Dazu stehen uns ICESat und ENVISAT Daten zur Verfügung. Unsere Aufgabe ist festzustellen ob es möglich ist, die ASAR Daten für Eisdickenklassifikation zu benutzen? Die ICESat Überflügsdaten werden bei der Validierung helfen. Wir fragen uns auch, im welchem Fehlerbereich diese Klassifikation möglich ist? __Ergebnisse__ Diskussion Hypothese: "Es ist möglich die Eisdicke/Freibordhöhe mittels ASAR Daten zu klassifizieren." "Die ICESat Daten werden uns dabei helfen, die klassifizierte Bilder zu validieren." Im welchem Fehlerbereich diese Klassifikation möglich ist? |
die Besprechung ergab fuer diese Gruppe:
- Trockenprogrammierung: insbesondere die Konsistenz von Bildkoordinaten von ASAR und Freibord-Footprint klären die Klasseneinteilungen von ASAR und Freibordhöhen vergleichen Frage "welche Statistik will man anwenden" beantworten
Dienstag
Am Dienstag / Mittwoch erzeugtes Programm, das mit dem Zufallsgenerator sowohl die ASAR als auch Freibord - Daten erzeugt:
1 #project_plot.py
2
3 from pylab import *
4 from scipy import *
5 import time,calendar,os,pipes,struct,string
6 import random
7 import scipy.ndimage as ndi
8 from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
9
10 nk=5 #number of classes
11 ndim=[1000,1000] #dimension of ASAR image in pixels
12 res=12.5
13 freeb_asar_pixels=int(60./res)# footprint of freeboard is 60m
14
15 fx0,fy0,fx2,fy2=[0.2,1.,1.,0.1]
16 fx0,fy0,fx2,fy2=fx0*ndim[0],fy0*ndim[0],fx2*ndim[0],fy2*ndim[0] # freeboard coordinates from input file
17 dist=sqrt((fx2-fx0)**2+(fy2-fy0)**2)*res
18 fdist=172 #distance of two freeboard footprints is 172m
19 nf=int(dist/fdist)
20
21 fz_h=zeros(nf) #fz_h is the freeboard heights
22 # produce a random array of freeboard heights
23 for i in range(nf):
24 fz_h[i]=random.random()*70
25
26 # the x,y positions of the freeboard footprints
27 if fx2==fx0:
28 fx=zeros(nf)+fx0
29 fy=linspace(0,ndim[1],nf)
30 else:
31 teta=(fy2-fy0)/(fx2-fx0)
32 fx=linspace(fx0,fx2,nf)
33 fy=(fx-fx0)*teta+fy0
34 #produce a random matrix of ASAR image classes (in 3 classes)
35
36 a=zeros((ndim[0],ndim[1]))
37 for i in range(ndim[0]):
38 for j in range(ndim[1]):
39 a[i,j]=int(random.random()*(nk)+1)
40
41 #tranform from float to int
42
43 #A=ndimage.gaussian_filter(a,1)+0.5
44 #B=A.astype(int)
45 B=a.astype(int)
46
47 #select the class of footprints from ASAR Image
48 fz=zeros(nf)
49 for i in range(nf):
50 fz[i]=B[int(fx[i]-1),int(fy[i]-1)]
51
52 #calculation of mean and standard deviation of freeboard heights in each class
53 mean=zeros(nk)
54 std_kl=zeros(nk)
55 for kl in range(1,6):
56 s=(fz==kl)
57 fh_kl=fz_h[s]
58 mean[kl-1]=fh_kl.sum()/fh_kl.shape[0]
59 std_kl[kl-1]=std(fh_kl)
60
61 #plot mean and error bar
62 kl=arange(nk)+1
63 bar(kl,mean,yerr=std_kl,ecolor='r',align='center')
64 axis('tight')
65 savefig('kl_mean_std', orientation='portrait', format='png')
66
67 #calculate correlation coefficient
68 #corr=xcorr(fz,fz_h,normed=True)[1][nf]
69
70 figure()
71 #plot ASAR image class together with freeboard heights
72 x=arange(nf)
73 bar(x,fz,width=0.3,align='center')
74 ylim(0,10)
75 ax=twinx()
76 plot(x,fz_h,'r+-',ms=10,linewidth=1)
77 ylim(0,70)
78 savefig('asar_fb', orientation='portrait', format='png')
79
80 #axis('tight')
81
82 #plot ASAR image with freeboard flight
83 figure()
84 ct=zeros((nf,4))
85 for i in range(nf):
86 ct[i]=cm.gist_rainbow(int(fz_h[i]))
87 ax=axes()
88 ells=[Ellipse(xy=[fx[i],fy[i]],width=freeb_asar_pixels,height=freeb_asar_pixels) for i in xrange(nf)]
89 n=0
90 for e in ells:
91 ax.add_artist(e)
92 e.set_clip_box(ax.bbox)
93 e.set_alpha(0.5)
94 e.set_facecolor(ct[n])
95 n+=1
96 gray()
97 imshow(B,origin='lower',interpolation=None)
98 hold(True)
99 #plot(fx,fy,'r+-',linewidth=2)
100 xlim(400,600)
101 ylim(500,700)
102 #xlim(0,1000)
103 #ylim(0,1000)
104 colorbar()
105 savefig('asar_fb_track', orientation='portrait', format='png')
106
107 #figure()
108 #imshow(a)
109 show()
Figure 1 (class - mean, standard deviation) / VIRTUELLE DATEN :
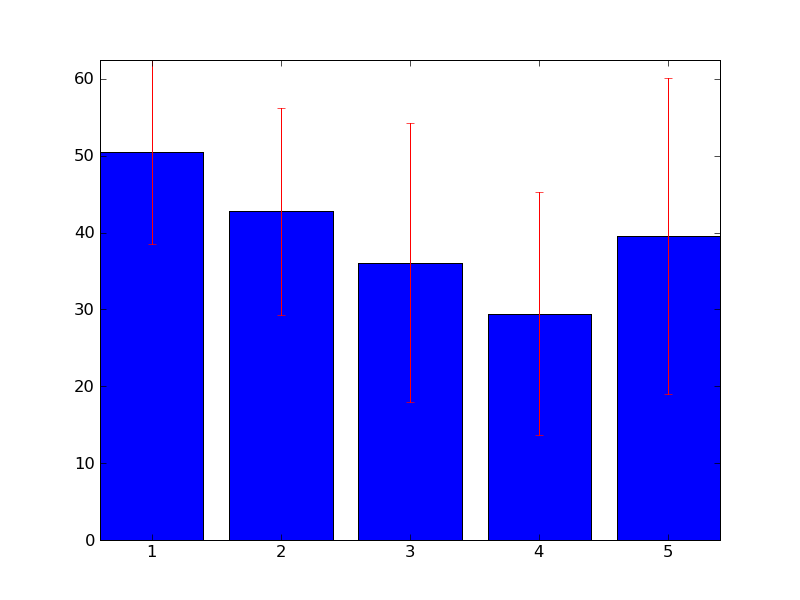
Figure 2 (asar, freboard) / VIRTUELLE DATEN :
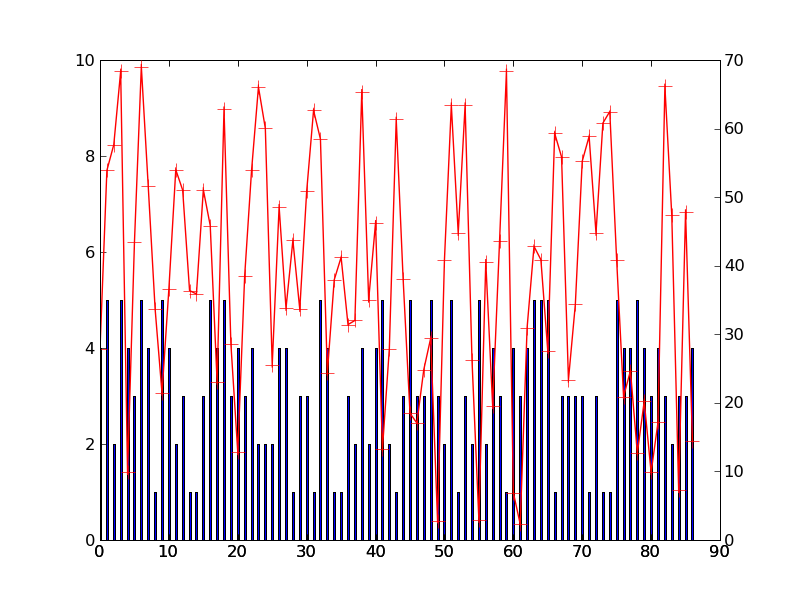
Ziele für Mittwoch:
- Vom gestern erzeugte Graphen verfeinen
Programm für ASAR-Rohdaten & Freiborddaten Vergleich
Mittwoch
Am Mittwoch erzeugtes Programm, das ASAR-Rohdaten und Freiborddaten (Zufallsgenerator), Faltungmaske 5x5 Pixel wurde benutzt:
1 #ASAR_raw.py
2
3 from pylab import *
4 from scipy import *
5 import time,calendar,os,pipes,struct,string
6 import random
7 import scipy.ndimage as ndi
8 from read_asar import *
9
10 filename='/pf/u/u242027/SAR_raw/ASA_IMP_1PNDPA20060617_043346_000000162048_00362_22460_2136.N1'
11 I=read_asar_imp(filename)
12
13 ndim=[1000,1000] #dimension of ASAR image in pixels
14
15 fx0,fy0,fx2,fy2=[200.,1000.,1000.,100.] # freeboard coordinates from input file
16 cellsize=12.5 #12.5m pixelsize
17 dist=sqrt((fx2-fx0)**2+(fy2-fy0)**2)*cellsize
18 fdist=172 #distance of two freeboard footprints is 172m
19 nf=dist/fdist
20
21 fz_h=zeros(nf) #fz_h is the freeboard heights
22 # produce a random array of freeboard heights
23 for i in range(nf):
24 fz_h[i]=random.random()*70
25
26 # the x,y positions of the freeboard footprints
27 if fx2==fx0:
28 fx=zeros(nf)+fx0
29 fy=linspace(0,ndim[1],nf)
30 else:
31 teta=(fy2-fy0)/(fx2-fx0)
32 fx=linspace(fx0,fx2,nf)
33 fy=(fx-fx0)*teta+fy0
34
35
36 B=I[1000:2000,1000:2000]
37
38 mask=array(([1,1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2,1],[1,2,3,2,1],[1,2,2,2,1],[1,1,1,1,1]))/35.
39 C=ndimage.convolve(B,mask,mode='reflect')
40
41 #select the intensity value of footprints from ASAR Image
42 fz=zeros(nf)
43 for i in range(nf):
44 pos=[int(fx[i]-1),int(fy[i]-1)]
45 fz[i]=B[pos[0],pos[1]]
46
47
48 #calculate correlation coefficient
49 corr=xcorr(fz,fz_h,normed=True)[1][nf]
50
51 figure()
52 #plot ASAR image intensity together with freeboard heights
53 x=arange(int(nf))
54 plot(x,fz,'b+-')
55 ax=twinx()
56 plot(x,fz_h,'r+-')
57 savefig('asar_fb_track_RAW', orientation='portrait', format='png')
58
59 #plot ASAR image with freeboard flight
60 #figure()
61 #plot(fx,fy,'r+-',linewidth=2)
62 #colorbar()
63 #imshow(B,origin='lower',interpolation=None)
64 #hold(True)
65
66 show()
Figure 1 (raw asar image, freeboard) / REELLE ASAR DATEN + VIRTUELLER FREIBORDDATENSATZ ::
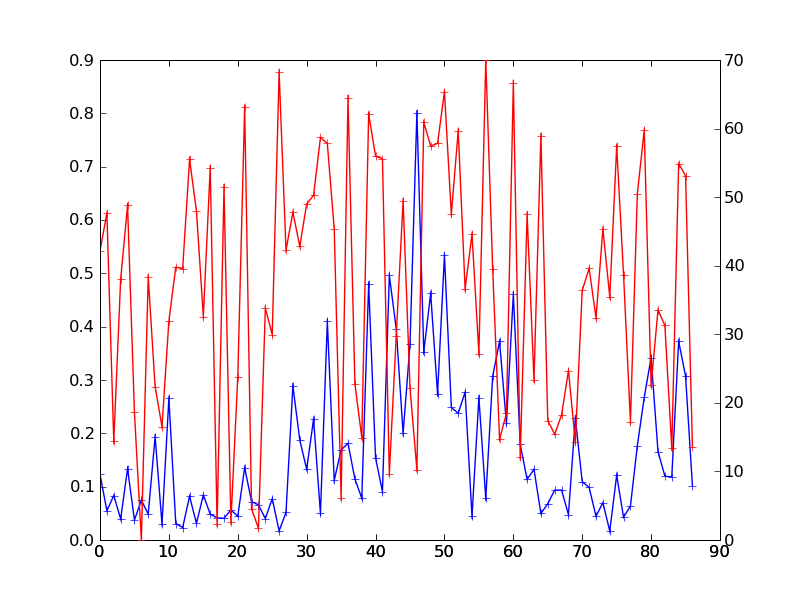
Ziele für Donnerstag:
- Farbtabelle für Freibordhöhen einbauen
- Programpaketen der anderen Gruppe übernehmen und ins Programm einbauen
- Testen und erste Ergebnisse liefern
- Bericht schreiben
Donnerstag
Am Donnerstag erzeugte Farbtabelle im 'project_plot.py' Program für Freibordhöhen:
Figure 3 (asar, freeboard track) / VIRTUELLE DATEN :
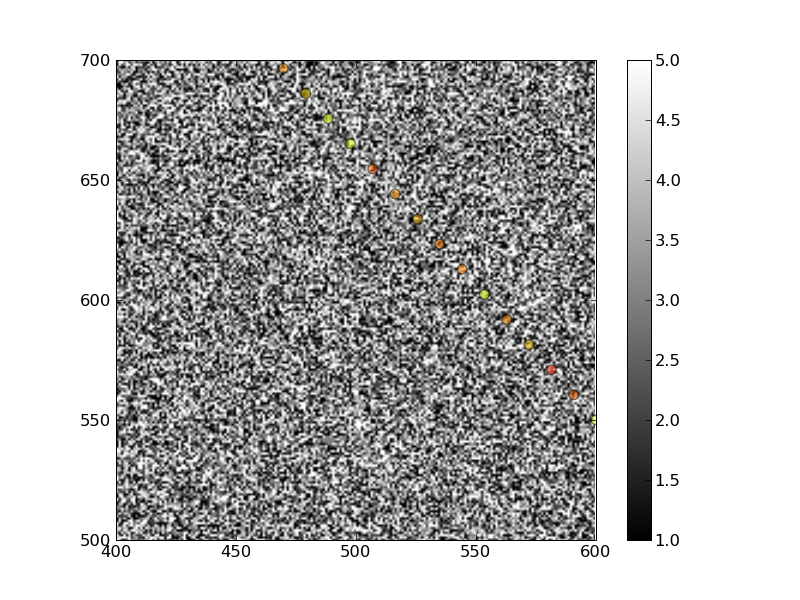
Berichtteil: # Motivation (Fragestellung) # Daten (ICESat, ENVISAT)
- - Zusammenbau Gruppe
Weil es am Beginn des Projektes noch keine Ergebnisse von den anderen Gruppen zur Verfügung gestanden sind, hat unsere Gruppe in den ersten Projekttagen mit den aus dem Zufallsgenerator erzeugten Daten gearbeitet. Mit dem Zufallsgenerator "random.random()" haben wir Freibordhöhen () und ASAR Bild (). heißt ...
# Methodik (Arbeitsschritten, Theorie, Input/Output)
- - Zusammenbau Gruppe
# Ergebnisse (Output, Statistik)
- - Zusammenbau Gruppe
Erste Gruppe hat eine Funktion geliefert x Zweite Gruppe hat ein Program geliefert
# Diskussion (Hypothese bestätigt, widerlegt?)
Motivation
Das Ziel von unserem Projekt ist es die Freibordhöhen im Gebiet des Weddellmeeres (Antarktis) zu klassifizieren. Dazu stehen uns ICESat und ENVISAT Daten zur Verfügung. Unsere Aufgabe ist festzustellen ob es möglich ist, die ASAR Daten für Eisdickenklassifikation zu benutzen? Die ICESat Überflügsdaten werden bei der Validierung helfen. Wir fragen uns auch, im welchem Fehlerbereich diese Klassifikation möglich ist?
Ergebnisse
Diskussion
Hypothese: "Es ist möglich die Eisdicke/Freibordhöhe mittels ASAR Daten zu klassifizieren." "Die ICESat Daten werden uns dabei helfen, die klassifizierte Bilder zu validieren." Im welchem Fehlerbereich diese Klassifikation möglich ist?
