|
Size: 4033
Comment:
|
Size: 4265
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 117: | Line 117: |
| [[Thermohaline Circulation|Content Here]] |
|
| Line 120: | Line 122: |
| === Meridional Overturning Circulation === | === Southern Ocean Circulation === [[Southern Ocean Circulation|Content Here]] |
| Line 125: | Line 129: |
| [[ENSO Response|Content Here]] |
|
| Line 128: | Line 134: |
| === Equatorial Wave === | === Equatorial Waves === [[Equatorial Waves|Content Here]] |
| Line 132: | Line 140: |
| === Significant Wave Height (Rayleigh distribution) === | === Rayleigh–Bénard Convection === [[Rayleigh–Bénard Convection|Content Here]] |
| Line 137: | Line 147: |
| [[Isopycnal Diffusion|Content Here]] |
Python Ocean Model (pyOM)
Contents
Introduction
A numerical Ocean Circulation Model to configure and to integrate idealized numerical simulations with python (GUI) and a standard Fortran90 frontend.
In both cases, the dynamical core of the model is written in Fortran90.
Features
- Surface pressure or implicit linear free surface formulation
- Non-hydrostatic version
- 1D domain decomposition for parallel computation
Assumptions and Approximations
- Neglecting of thermodynamic equation
- Boussinesq approximation
- ( Volume conservation and Buoyancy perturbations in gravity term)
- Cartesian and beta-plane approximation
Resources
Prerequisites and Installation
Prerequisites
1. Unix system
2. Fortran 90 compiler
3. Fortran and Python front ends NetCDF-library
Installation
1. Make a new directory where the model code should be placed. Name the directory as dir(for instance)
2. Get into the remote server thunder1 (Only for students in UHH)
ssh thunder1
3. Once you log in, find u241155 (Prof. Eden directory)
finger u241155
and copy this directory to your new directory to get src file for compiling.
cp home/zmaw/u241155/pyOM_thunder
4. Then, by different Fortran subroutines and Python methods in the model configuration
environments in specific realizations can be shown.
List of Directories
* ./for_src: Fortran subroutines used by both Fortran and Python front end
* ./py_src: Python modules and extension modules
* ./py_config: Configuration examples of Python front end
* ./for_config: Configuration examples for Fortran front end
* ./doc: contains documentation
* ./bin: contains executable of Fortran front end after successful compilation
Model Configurations
Allocating the model variables
* set_parameter :sets all important fixed model parameter
In the model setup
* set_coriolis : sets the (vertical and horizontal) Coriolis parameter.
* initial_conditions :sets the initial conditions.
* topography : set the topography.
For each time step
* boundary_conditions : set the surface boundary conditions.
* restoring_zones : set the interior sources and sinks for density.
* momentum_restoring_zones : set the interior sources and sinks for momentum.
* tracer_sources : set interior sources and sinks for the passive tracer. Also sets the surface boundary conditions.
Sample Configurations
Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability
kelvin_helm1.py
Eady's Baroclinic Instability
eady1.py / eady2.py
Eddy-driven zonal jets
jets1.py
Thermohaline Circulation
THC1.py
Southern Ocean Circulation
acc1.py
ENSO Response
enso1.py
Equatorial Waves
eq_waves1.py
Rayleigh–Bénard Convection
rayleigh.py
Isopycnal Diffusion
isopyc_test1.py
//pyOM (Python Ocean Model)
is a numerical ocean circulation model with an easy to use python (GUI) and a standard
Fortran90 frontend. In both cases, the dynamical core of the model is written in Fortran90.
Some features are
- surface pressure or implicit linear free surface formulation
- nonhydrostatic version
- 1D domain decomposition for parallel computation
Documentation available as pdf file
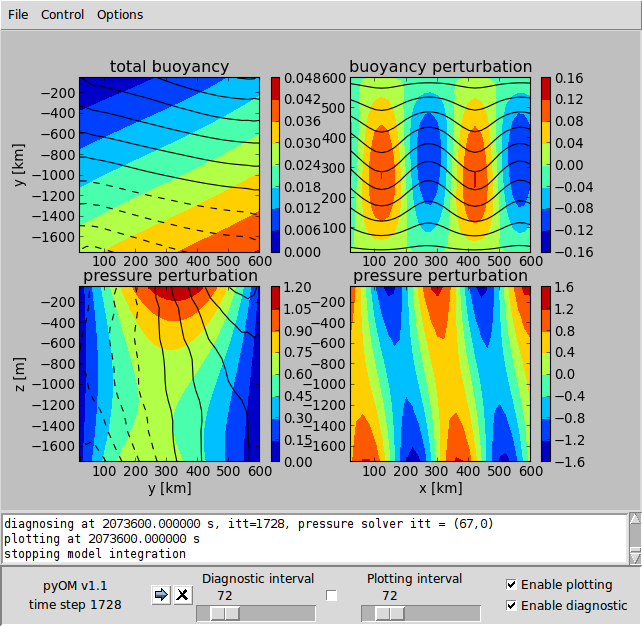
An example of the python GUI for Eady's baroclinic instability case is shown below.
Source code pyOM_1.1.tar.gz
