|
Size: 4111
Comment:
|
Size: 3891
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 46: | Line 46: |
| == Increase of sea ice drift velocity == | == Summary == |
| Line 50: | Line 51: |
| * Surface air temperature increased by 3°C since 1987 * Wind speed increased by 0.6 m/s since 1950 * Ice drift speed doubled since 1950 * September area decreased by 40% since 1990s * ~50% reduction of ice thickness in the transpolar drift since 2001 * Interannual thickness variability ~20% mainly controlled by thermodynamics * Model suggests thinning since 1987 at a rate of -20%/decade * 2007 ice extent strongly anomalous, ice mass loss not * Close to tipping point? |
|
| Line 51: | Line 61: |
| == Increase of temperature and wind speed, decrease of pressure == Based on NCEP {{attachment:temp_anom.png}} {{attachment:wind_anom.png}} {{attachment:pres_anom.png}} |
== Questions == * How large is the internal variability? * Quality of data? * Reliability of models? |
| Line 69: | Line 75: |
== Summary == * Surface air temperature increased by 3°C since 1987 * Wind speed increased by 0.6 m/s since 1950 * Ice drift speed doubled since 1950 * September area decreased by 40% since 1990s * ~50% reduction of ice thickness in the transpolar drift since 2001 * Interannual thickness variability ~20% mainly controlled by thermodynamics * Model suggests thinning since 1987 at a rate of -20%/decade * 2007 ice extent strongly anomalous, ice mass loss not * Close to tipping point? == Questions == * How large is the internal variability? * Quality of data? * Reliability of mode? |
Contents
CliSAP Working Group Arctic Variability
Sprecher/Kontakt Lars Kaleschke
Ziele
Die CliSAP-Arbeitsgruppe "Arktische Variabilität" (AV) versteht sich als Basis für die instituts- und projektübergreifende Kommunikation zu dem Themenkomplex Klimawandel in der Arktis. Um die Kommunikation in Gang zu bringen, werden Arbeitstreffen zu bestimmten Themen in einem 4-8 wöchigen Rhythmus organisiert. Diese für alle Interessierten offenen Treffen sollen durch einen etwa 15-minütigen Impulsvortrag eingeleitet werden. In der darauf folgenden etwa 45-minütigen Diskussion sollen folgende Fragen beantwortet werden: Wer arbeitet an diesem Thema? Wie ist der aktuelle Stand des Wissens? Was sind die brennenden offenen Fragen?
Themen
- Wasser- und Energiebudget der Arktis (hydrologischer Kreislauf, Eisvolumen und -transport, Albedo)
- Interne Variabilität
- Response auf Variationen des externen Forcings (CO2, solare Einstrahlung, Vulkane)
- Biogeochemie der Arktis
- Schmelzen von Grönland
- Vermischungsprozesse auf dem Schelf
- Austausch Schelf-Ozean
- Numerik (Advektion, Meereismodellierung)
- Parametrisierungen für heterogene Grenzflächen
- Nicht hinreichend verstandene Prozesse (Meereis, Wolken)
- Permafrost/Gashydratdissoziation
Permafrost April/Mai 2009 (Lars Kutzbach)
Interne Variabilität 10. März 2009 (Johann Jungclaus, Dirk Notz)
- Multidekadische Variabilität
- Die Erwärmung in den 1930ern
The rapid retreat of Arctic sea ice 1.12.2008 (Lars Kaleschke, Dirk Notz, Nuno Serra)
Summary
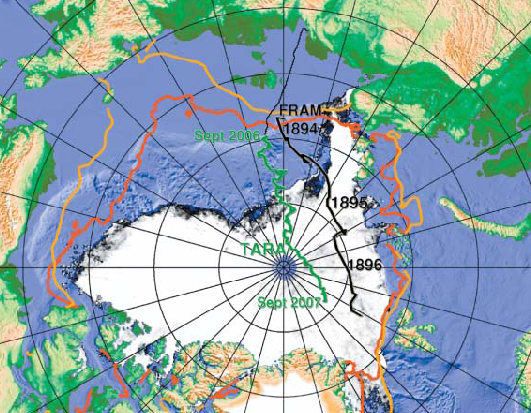
- Surface air temperature increased by 3°C since 1987
- Wind speed increased by 0.6 m/s since 1950
- Ice drift speed doubled since 1950
- September area decreased by 40% since 1990s
- ~50% reduction of ice thickness in the transpolar drift since 2001
- Interannual thickness variability ~20% mainly controlled by thermodynamics
- Model suggests thinning since 1987 at a rate of -20%/decade
- 2007 ice extent strongly anomalous, ice mass loss not
- Close to tipping point?
Questions
- How large is the internal variability?
- Quality of data?
- Reliability of models?
